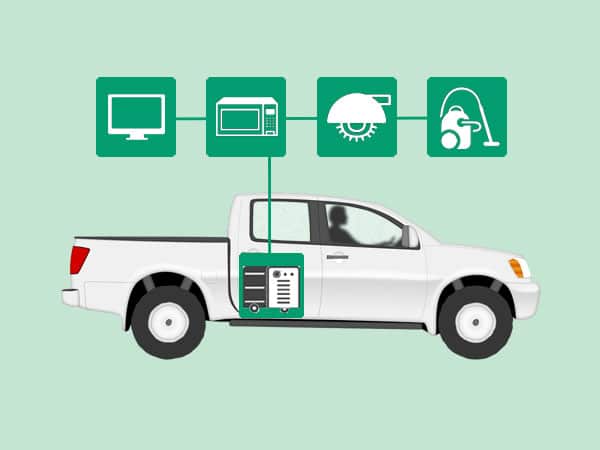
My friend owns a Ford F150 raptor so on the long trips he misses the grid supply dependent equipment such as his laptop, and power tools. So being an electronics engineer myself and a tinkerer too, I got to help him sort this out. So I researched how to get a grid power supply to his truck without spending a fortune for a generator set which also takes much space of the truck bed. This is how I learned to install an inverter in a truck bed.
Now with those research results, I think I should write a blog to help out many people with similar problems out there. So out of many options, a viable one is to convert the existing engine power to the grid power.
So how do we convert the engine power to the grid equivalent power? My research revealed that by using a simple inverter, we could transform the existing engine power of 12 volts to an Alternating 110 volts at 60Hz, which is in fact grid supply. The inverter is very slim and can supply up to 4000 Watts.
But there are more to this. What if we want to use sensitive equipment with the inverter? Are there some standards for these inverters? How do we install them in the truck bed or what is the best place to install an inverter in the truck? Now let’s dive into the ultimate guide for how to install the inverter in a truck bed.
Table of Contents
What Should be the Power Rating of the Inverter you have to Buy
Let’s calculate what should be the power rating of the inverter you have to buy. So before we finally decide to purchase an inverter for your truck, first determine how much power you want to consume. Below there is a rough estimation of how much power required for equipment needing grid supply. So add up the things you want to use at once and add 30% more to prevent overload on the inverter.
| Electrical Equipment | Approximate minimum Wattage | Approximate maximum wattage | Standby mode wattage |
| 25″color TV | 150W | 150W | N/A |
| 3″ belt sander | 1000W | 1000W | N/A |
| Light bulb 60W (Incandescent) | 60W | 60W | 0W |
| 9″ disc sander | 1200W | 1200W | N/A |
| Ceiling Fan | 25W | 75W | 0W |
| Clock radio | 1W | 2W | N/A |
| Clothes Dryer | 1000W | 4000W | N/A |
| Coffee Maker | 800W | 1400W | N/A |
| Cordless Drill Charger | 70W | 150W | N/A |
| Desktop Computer | 100W | 450W | N/A |
| Dishwasher | 1200W | 1500W | N/A |
| Electric Blanket | 200W | 200W | N/A |
| Electric Heater Fan | 2000W | 3000W | N/A |
| Electric Kettle | 1200W | 3000W | 0W |
| Electric Mower | 1500W | 1500W | N/A |
| Electric Shaver | 15W | 20W | N/A |
| Food Blender | 300W | 400W | N/A |
| Fridge / Freezer | 150W | 400W | N/A |
| Game Console | 120W | 200W | N/A |
| Hair Blow-dryer | 1800W | 2500W | N/A |
| Home Air Conditioner | 1000W | 4000W | N/A |
| Home Internet Router | 5W | 15W | N/A |
| Hot Water Immersion Heater | 3000W | 3000W | N/A |
| Inkjet Printer | 20W | 30W | N/A |
| Inverter Air conditioner | 1300W | 1800W | N/A |
| Iron | 1000W | 1000W | N/A |
| Laptop Computer | 50W | 100W | N/A |
| Lawnmower | 1000W | 1400W | N/A |
| LED Light Bulb | 7W | 10W | 0W |
| Microwave | 600W | 1700W | 3W |
| Oven | 2150W | 2150W | N/A |
| Power Shower | 7500W | 10500W | 0W |
| Rice Cooker | 200W | 250W | N/A |
| Scanner | 10W | 18W | N/A |
| Smart Phone Charger | 4W | 7W | N/A |
| Strimmer | 300W | 500W | N/A |
| Submersible Water Pump | 400W | 400W | N/A |
| Table Fan | 10W | 25W | N/A |
| Tablet Charger | 10W | 15W | N/A |
| Tablet Computer | 5W | 10W | N/A |
| Toaster | 800W | 1800W | 0W |
| TV (19″color) | 40W | 100W | 1W |
| Vacuum Cleaner | 200W | 700W | 0W |
| Washing Machine | 500W | 500W | N/A |
| Water Dispenser | 100W | 100W | N/A |
| Water Feature | 35W | 35W | N/A |
| Water Filter and Cooler | 70W | 100W | N/A |
Continues Power vs. Peak Power Rating for Inverters
Keep in mind that the figure we obtained from the above calculation needs a steady power output to supply good power for our equipment. There are two types of power ratings available on the inverters, called steady power and surge power. Be aware of some cheap inverters which don’t mention power ratings and may cause a fire from overheating or overloading.
Now Let’s know what is steady or continues power rating. Continues power rating is the capacity of the inverter to supply the rated power continuously without overheating or tripping for long durations. Loads like LED TV, DVD player music systems, game consoles, heaters, light bulbs need continues power consumption. While surge power is where some equipment needs a large amount of energy for a short burst of time like various power tools, laser printers, etc.
How Much Output Power is Same as Grid Power?
We receive the grid power in an alternating sine wave which comes from generating stations which are an actual sine wave. But our truck has 12 volts direct current available to the converter. So output must be identical or nearly identical to the grid supply; especially to drive power sensitive equipment. There are mainly two types of output power shape, i.e., Pure Sine Wave and Modified Sine Wave.
- Pure sine wave output is identical to supply grid wave and are perfect for running various sensitive equipment like LED TV, laptops, etc. as they run smoothly. Motorized equipment also runs silent, without vibration or humming noise and have prolonged service duration. These are expensive than inverters having modified sine wave output, but the increased price justifies the added advantages.
- Modified sine wave output is not pure sine wave but additions of various amplitudes of a square wave. These are never suitable for driving sensitive types of equipment and produce heat and humming noise due to the presence of nth order harmonics in the motorized kind of machine which also reduces service life. But Such inverters come cheaper then inverters having pure sine wave output.
Is There Any Safety Ratings for Such Inverters?
As we are installing it on a moving vehicle and using it on rough highways, we have to ensure that we buy an inverter which has features such as overloading protection, overheating protection, short circuit protection, and battery over discharge protection. There is a certification from UL which is a global independent safety science company which certifies such consumable equipment.
If an inverter has UL-458 on it, then go for it because on mobile or standing condition we don’t need a fire hazard onboard. A dead battery will leave us stranded in the middle of the road because we opted for a cheaper inverter which doesn’t have such safety ratings. Now that we know what type of inverter we need let’s move on to the other equipment we need.
What is the Equipment we Need to Set Up the Inverter?
Warning! Be careful while handling power tools and always use proper safety measures while handling such devices. Do not short circuit the battery; it may cause severe harm and damage to the battery and associated circuitry. It may even cause a fire. We don’t want to end up with a dysfunctional truck if you are not sure you can get it installed by professionals.
Cable:
Go for the best quality cable possible because it will carry around all the power from your battery to your inverter. We don’t want resistance to paving the path of current flow. So the cable width is measured in AWG(American wire gauge) standard. The lower the AWG, the better the cable can carry power from battery to inverter without losses.
Let’s get into Wire Gauge Chart.
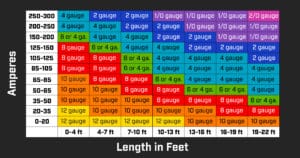
There are Amperes in the left and cable length in the bottom. So use this simple formula to calculate your approximate cable length
Current (in Ampers) = Rated power on inverter(in watts)/ 12 volts.
Use the current value obtained from above to find out the gauge value for the cable depending on the length you need. Also, cut the wire keeping extra 5% to 10% of original length. The best AWG without any messy calculation is 0 AWG without thinking. 0 AWG is the most heavy duty cable and supports upgrade in inverter with more power if you ever want the extra energy in the future. Do not forget to get red and black wire which is the industry standard. It will ease up inverter maintenance and troubleshooting in the future.
Cable Terminal Connectors:
These are the end connectors for a cable which connects both ends of the wire to battery and inverter. We can use Screw Battery Ring Terminals or Crimpable battery terminals. Make sure to use good quality to avoid corrosion in the connectors and battery terminals.
Screw Battery Ring Terminals are best for home installation if you don’t have a crimping tool.
Fuse Block Terminal with Fuse:
We don’t want fire in our engine bay or melted cables in case of a short circuit. It will damage the truck battery as well as the inverter. So we need a fuse inline with the positive wire. The fuse rating should be equal to the amperage rating we have previously calculated.
Battery Isolator Switch:
We need to stop an excessive drain on the battery when we are not using the inverter. We will use a battery isolator switch to disconnect the inverter.
Other Necessary Items:
- Drilling machine
- Cable Gland Connector with Locknut
- Zip ties, Extra batteries if you are planning to put a heavy load on the inverter
- Battery isolator to isolate the Auxilary battery from the main battery
- Screwdrivers
- Electrical petroleum jelly to prevent the connections from getting corrosion
- Necessary car repair tools, etc.
Now let’s Start installing the inverter in our truck. We will go through the steps one by one.
Step-1:
Before installing the inverter let’s have a blueprint where we put our components. Let’s decide for the parts that will go into the engine bay and the location for the inverter in the truck bed. First We have to prepare and cut the cable to its appropriate lengths.
Step- 2:
We must decide where to mount our inverter. The best place is inside the bed wall which is quite easy to reach. You can choose other areas like in the left or right quarter panel of the truck too. We should have a solid ground wire connected from inverter up till the negative terminal of the battery and a positive solid cable connected from inverter positive terminal up to the battery isolator switch.
Step- 3:
We have to figure out how we will route the wire through the cabin up to the battery. If we can make it around the cab, we don’t have to put any holes in our cabin. Then we don’t have to worry about waterproofing the cabin. If we choose to run the cable through the cabin, then we have to put three pairs of holes through the cab; a couple in the truck bed, a pair on backside or underside of the cab depending on suitable places to draw the wire in without much of hassle.
Then the last couple in the firewall between the engine bay and cab to make the cable up to the battery. The fuse: This is the first component and easy to install too. We will connect it directly to battery and Battery isolator switch along the positive cable rail.
Step- 4:
Now we have to find a place in the engine bay to mount the battery isolation switch and fuse. It depends on the type of parts you have purchased. Drill holes in the engine bay to properly mount the components, Don’t trust on glues ever! Always use mounting screws as recommended by parts manufacturer.
Step- 5:
Let’s mount the inverter in the truck bed by screwing it properly. Double check for wiggles or movements as it may damage the inverter internals.
Step-6:
Then we have to route the wires through the cabin or around the cabin. If routing through the cabin, we have to seal the exit points and entrance points with waterproof seeling glue, or we can use cable gland connector with locknut; which has inbuilt rubber to keep the water out of the cabin.
Step- 7:
Let’s cut the ends of both cable and connect them to the cable terminal connectors. We need four of them, two for connecting the inverter and another two for the battery ground and battery cutoff switch.
Step- 8:
Let’s mount the battery cutoff switch and battery cutoff fuse in their planned places. Take another piece of cable to connect the switch and fuse using terminal connectors.
Step- 9:
Now the final step. Let’s connect the fuse to battery positive terminal using cable and termination connector. You can connect it directly depending on the type of fuse you have purchased. Then join the ground wire to the battery.
Step-10:
Now it is time to test our setup. Let’s toggle the battery cutoff switch to on position and turn on the inverter and start using it.
Now you have a truck which can supply, run and drive grid dependent equipment on the go. Pretty nifty huh!
Related Questions
Can my Inverter Recharge my Battery?
Yes, of course, you can. Just buy an inverter which has the battery charging capability. The additional battery adds more power and elongates battery life. The cells used in trucks are not deep cycle battery, means you can’t use them down to 11.3 volts. These have very thick electrodes to put as much as possible current for a short time like during ignition. So if the inverter has reverse charging capability, you can charge it out at gas stations and usual wall outlets.
What if I Mount the Second Battery to the System, Is it Even Possible?
Yes, it is possible. We can add a second battery to support the primary battery. We have to install an additional battery before battery isolator switch so that either of our cells won’t charge each other which is terrible for both the battery.
Conclusion
Installing an inverter can get expensive, depending on the type of tools you want to use with the inverter. But, in general, a truck bed inverter is best for running tools that need a short burst of power. That said, you should totally avoid installing an inverter on your own if you are not knowledgeable and skilled enough to know the requirements of the installation and its inner workings.

With a wrench in one hand and a trucker’s hat on my head, I’ve been knee-deep in the world of trucks for over a decade. From tinkering in greasy garages to cruising down open highways, my life has been one big trucking adventure. I’ve hauled, repaired, and revved up more rigs than I can count, and now I’m revving up your truck knowledge with articles that’ll steer you right.